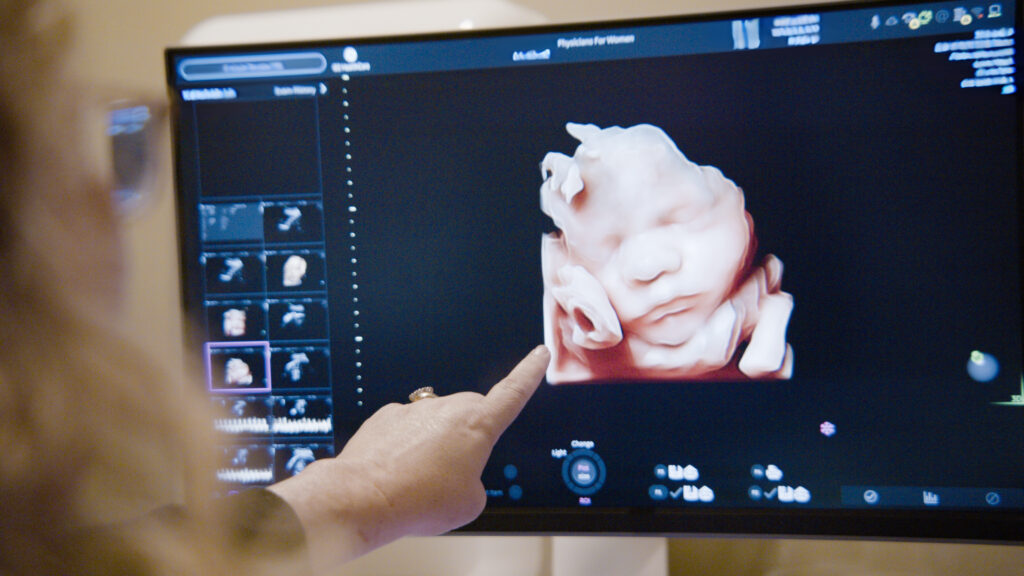
Welcome to Physicians for Women!
Welcome to Physicians for Women, where compassionate care for your health and well-being is our top priority. Our devoted team of OB/GYNs and nurse practitioners is here to support you through every stage of your life. We are committed to nurturing, empowering, and providing you with the highest quality medical expertise, all delivered with warmth and understanding.

Our Mission
At Physicians for Women, we understand that every woman is unique, and we’re dedicated to creating a healthcare experience that reflects that individuality. Our mission is rooted in compassion; we believe that each woman deserves care that is as special as she is. More than just medical treatments, we are here to uplift your overall well-being, providing a warm and nurturing environment where you feel genuinely valued and understood. We are committed to supporting you in making informed choices about your health, ensuring that you never feel alone with your healthcare.

Physicians for Women
Obstetricians & Gynecologists & Physicians located in Fitchburg, WI
The motto of our clinic is simple yet profound: “It’s not the number of women we treat, it’s how we treat women.” We put this practice in place to guide everything that we do, from the personalized needs and services we provide for each patient to the genuine kindness our staff brings to every interaction. We invite you to experience the difference at Physicians for Women, where your well-being is our top priority.
Insurance Accepted
Meet the Team
Our team at Physicians for Women brings together a diverse tapestry of talents, each thread carefully chosen to create a comprehensive picture of care. From our seasoned OB/GYN physicians with years of experience in complex procedures to our nurturing nurse practitioner, every member of our staff is dedicated to weaving comfort, expertise, and personalized attention into your healthcare journey.
Read More
Each physician on staff at Physicians for Women brings years of experience in obstetrics and gynecology to the practice. All are board-certified, and many have undertaken additional education and training in various areas of expertise.
Physicians for Women also has Midwives so patients have access to midwifery services if they desire.
Well-woman exams are a cornerstone of the practice, and top-quality obstetrics care is another area of specialty. Services range from in-office hysteroscopy and colposcopy to minor gynecologic surgical procedures. Full-spectrum ultrasound 4D technology with the Voluson® platform delivers outstanding imaging.
Whether you’re searching for a new gynecologist, preparing to welcome a new baby into your family, or need top-quality care for a complex gynecology need, the team at Physicians for Women can meet your needs and exceed your expectations.
The practice motto is, “It’s not the number of women we treat, it’s how we treat women.” In an environment in which healthcare is becoming more rushed and less personalized, the specialists at Physicians for Women embrace a more traditional approach in which doctors get to know the women in their care and build relationships that endure through the phases of life.
Why choose Physicians for Women?
At Physicians for Women, we truly believe that outstanding healthcare goes beyond just medical treatments. Our team is dedicated to providing personalized, compassionate care that caters to the unique needs of every patient. Whether you see us for routine check-ups or specialized treatments, we always prioritize your comfort and well-being.
Our Madison-area practice offers high-quality women’s healthcare in a modern and friendly atmosphere. It is our goal to ensure that you never feel like just a number, you feel welcome and confident in your care. Our clinic includes board-certified OB/GYNs, and nurse practitioners, who are up to date with the latest research, procedures, and technology, providing you with the best care available in Madison.
Selecting the right healthcare team is a very important and personal decision. Discover why Physicians for Women stands out as a beacon of excellence in the realm of obstetrics and gynecology.
- Your Needs, Under One Roof
- A Team That Listens with Their Hearts
- Advanced Care with a Personal Touch
- Sharing in Your Goals
- Your Lifelong Health Companion
Your Needs, Under One Roof
Picture a place where all your women’s health needs are met under one roof. That’s the reality at Physicians for Women. Our practice is a harmonious blend of diverse specialties, from the joys of pregnancy to the nuanced care of gynecological health. We offer a wide range of services including high-risk pregnancy management that turns challenges into triumphs, state-of-the-art 4D ultrasounds that bring your baby’s first portrait to life, and tailored menopause treatments that help you transition into a new phase of life.
A Team That Listens with Their Hearts
At Physicians for Women, you’ll find more than just medical professionals; you’ll discover compassionate allies in healthcare. Our OB/GYNs and nurse practitioners are experienced in their fields, creating care plans that resonate with your unique needs. We believe in the power of attentive listening, taking the time to hear the subtleties of your concerns and crafting solutions that align perfectly with your life.
Advanced Care with a Personal Touch
At Physicians for Women, we use the most up-to-date technology and evidence-based care, while never losing sight of the human touch. Our practice is a fusion of advanced technology and warm, personalized care. From our cutting-edge 4D ultrasound capabilities that offer a window into your growing baby’s world to our gentle C-section techniques that prioritize your comfort and recovery, we’re constantly trying to improve what’s possible in women’s healthcare.
Sharing in Your Goals
We see you as a whole person, not just a set of symptoms. Whether you’re seeking preventive care to maintain your health, managing a complex health condition, or embarking on the path to motherhood, our comprehensive support system addresses every facet of your physical, emotional, and reproductive health.
Your Lifelong Health Companion
Physicians for Women is there for you in every stage of your life. From annual visits to pregnancy to managing menopause, we can offer the most up-to-date advice backed by evidence-based care. We have providers across multiple disciplines that are very experienced in their fields. Our goal is to make you feel comfortable and to feel like you are being heard with both good news and concerns.
Conditions & Treatments
How can we help?
All General Services at Physicians for Women
What is an IUD Insertion?
An IUD insertion is a medical procedure where a small, T-shaped device is placed inside the uterus to provide long-term contraception. The intrauterine device (IUD) can be either hormonal or copper-based, and it works by preventing sperm from fertilizing an egg. At Physicians for Women, we perform IUD insertions with precision and care, often using ultrasound guidance to ensure accurate placement. This procedure is a popular choice for women seeking an effective, low-maintenance birth control method.
How an IUD Insertion is Performed
During an IUD insertion at Physicians for Women, the healthcare provider will first review your medical history and perform a pelvic exam. The cervix is gently opened, and the IUD is inserted through a thin tube into the uterus. Ultrasound guidance may be used to visualize the uterus and ensure the IUD is positioned correctly. The entire process takes just a few minutes, and while some women may experience mild discomfort or cramping, the procedure is generally well-tolerated. After insertion, the provider will check the placement and provide aftercare instructions to ensure the IUD remains effective and comfortable.
Benefits and Considerations of an IUD Insertion
An IUD insertion offers several benefits, including long-term contraception that can last between 3 to 10 years depending on the type of IUD. This method is highly effective, with a success rate of over 99%. It is also convenient, as it requires no daily attention and is reversible when you decide to conceive. At Physicians for Women, we ensure the process is as comfortable as possible, using ultrasound guidance to minimize risks and enhance accuracy. This advanced technique is particularly beneficial for women with complex uterine anatomy or those who have had previous unsuccessful IUD insertions.
Common Conditions and Symptoms Managed with an IUD Insertion
- Heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Painful periods.
- Endometriosis-related pain.
- Need for reliable, long-term contraception.
- Irregular menstrual cycles.
Key Features of an IUD Insertion
- Long-term contraception lasting 3 to 10 years.
- High effectiveness rate over 99%.
- Minimal maintenance once inserted.
- Reversible, allowing for future conception.
- Option of hormonal or non-hormonal (copper) IUDs.
Preparing for Your IUD Insertion
- Schedule a consultation to discuss your options with a healthcare provider.
- Undergo a pelvic exam to ensure you are a good candidate for an IUD.
- Plan for mild discomfort during the procedure and arrange for rest afterward.
- Discuss any concerns or questions you have with your provider.
- Follow aftercare instructions to ensure the IUD remains effective and comfortable.
Emotional and Physical Impact of an IUD Insertion
An IUD insertion can significantly impact both your emotional and physical well-being. Physically, it provides a reliable and hassle-free contraceptive method, reducing the need for daily pills or frequent clinic visits. Emotionally, knowing you have a highly effective form of contraception can provide peace of mind and allow you to focus on other aspects of your life. At Physicians for Women, our goal is to ensure you feel supported and informed throughout the process, making the experience as positive and comfortable as possible.

Understanding Post and Pre Operation Care
Post and pre operation care refers to the comprehensive care provided before and after a surgical procedure. Pre operation care includes all preparations necessary to ensure a patient is ready for surgery, such as medical evaluations, instructions on fasting, and what to expect on the day of surgery. Post operation care involves managing recovery, monitoring for complications, and ensuring the patient follows their post-operative instructions. At Physicians for Women, our team is dedicated to offering thorough and compassionate care to help you feel confident and supported throughout your surgical journey.
Pre Operation Care Procedures
During pre operation care at Physicians for Women, your healthcare provider will conduct a detailed medical evaluation to assess your readiness for surgery. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, and a review of your medical history. You will receive specific instructions on how to prepare for the surgery, including fasting guidelines, medication adjustments, and what to expect on the day of the procedure. This phase is crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring a smooth surgical experience.
Post Operation Care Procedures
Post operation care at Physicians for Women focuses on monitoring your recovery and managing any pain or discomfort. The healthcare team will provide detailed instructions on wound care, activity restrictions, and signs of potential complications to watch for. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor your progress and address any concerns. Effective post-operative care is essential for preventing complications and ensuring a swift and complete recovery.
Addressing Key Conditions and Symptoms with Post and Pre Operation Care
- Pre-surgical anxiety and stress.
- Post-surgical pain and discomfort.
- Wound care and infection prevention.
- Monitoring for complications such as bleeding or swelling.
- Managing medication adjustments.
Key Features of Post and Pre Operation Care
- Comprehensive medical evaluations before surgery.
- Detailed preparation instructions to ensure readiness.
- Personalized post-operative care plans.
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor recovery.
- Education on signs of complications and how to manage them.
Preparing for Your Operation
Preparing for your operation involves several important steps to ensure you are ready for the procedure and the recovery period. At Physicians for Women, we guide you through each step, providing all necessary information and support. You will receive instructions on fasting, medication adjustments, and what to bring on the day of surgery. Our team is here to answer any questions and help alleviate any concerns you may have.
Comprehensive Support Before and After Surgery
The comprehensive support provided before and after surgery plays a crucial role in your overall experience and recovery. Emotionally, a well-structured care plan helps reduce anxiety and stress associated with surgery. Physically, proper preparation and diligent post-operative care can minimize complications and promote faster healing. At Physicians for Women, we strive to create a supportive environment where you feel empowered and informed throughout your surgical journey.

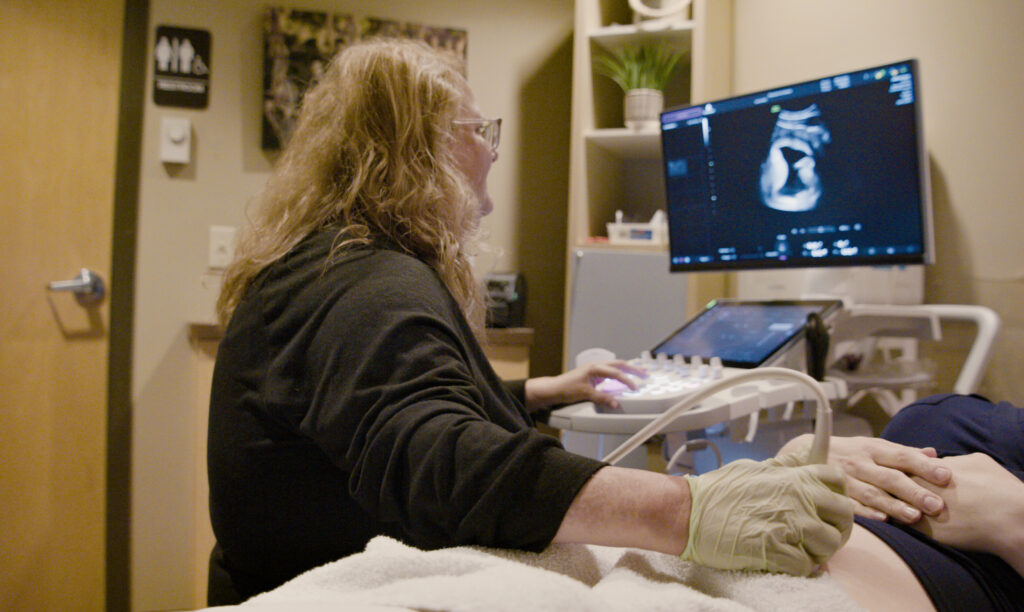
What is an Ultrasound?
An ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of structures within the body. This technology is widely used in medical settings to monitor pregnancies, diagnose conditions, and guide certain procedures. At Physicians for Women, ultrasounds are a crucial tool in providing comprehensive care. The procedure is safe and painless, allowing healthcare providers to see detailed images of organs, tissues, and the developing fetus without the need for radiation.
How Ultrasound is Used
Ultrasound is utilized in various medical scenarios, most notably in prenatal care to monitor the growth and development of the fetus. It helps in detecting abnormalities, assessing the health of the baby, and determining the due date. Besides obstetrics, ultrasounds are also used to diagnose conditions related to the heart, liver, kidneys, and other organs. At Physicians for Women, we employ advanced ultrasound technology to ensure accurate diagnoses and effective monitoring, enhancing the overall quality of care provided to our patients.
Benefits of Ultrasound
The primary benefits of ultrasound include its non-invasive nature and its ability to provide real-time images. This makes it an ideal tool for monitoring fetal development throughout pregnancy, as well as diagnosing a variety of medical conditions. Ultrasounds can detect issues early, allowing for prompt treatment. At Physicians for Women, our ultrasound services are designed to offer detailed insights into your health, helping to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mothers and their babies.
Key Features of Ultrasound
- Non-invasive and painless.
- Provides real-time imaging.
- No radiation exposure.
- High accuracy in detecting abnormalities.
- Widely used in prenatal care and diagnostics.
Preventive Aspects of Ultrasound
- Early detection of fetal abnormalities.
- Monitoring of fetal growth and development.
- Identification of potential complications.
- Assessment of organ function and structure.
- Guiding minimally invasive procedures.
Comprehensive Ultrasound Care
At Physicians for Women, our comprehensive ultrasound care ensures that you receive accurate and timely information about your health. Our skilled technicians and healthcare providers work together to interpret ultrasound images, providing you with detailed explanations and next steps. Whether you are undergoing an ultrasound for prenatal care or to diagnose a medical condition, our team is committed to offering professional and compassionate care.
Enhancing Patient Experience with Ultrasound
Ultrasound not only provides vital information but also enhances the patient experience by offering a non-invasive and comfortable diagnostic option. At Physicians for Women, we prioritize your comfort and ensure that each ultrasound procedure is conducted with the utmost care. Our goal is to make your experience as pleasant and informative as possible, helping you to feel confident and supported throughout your healthcare journey.
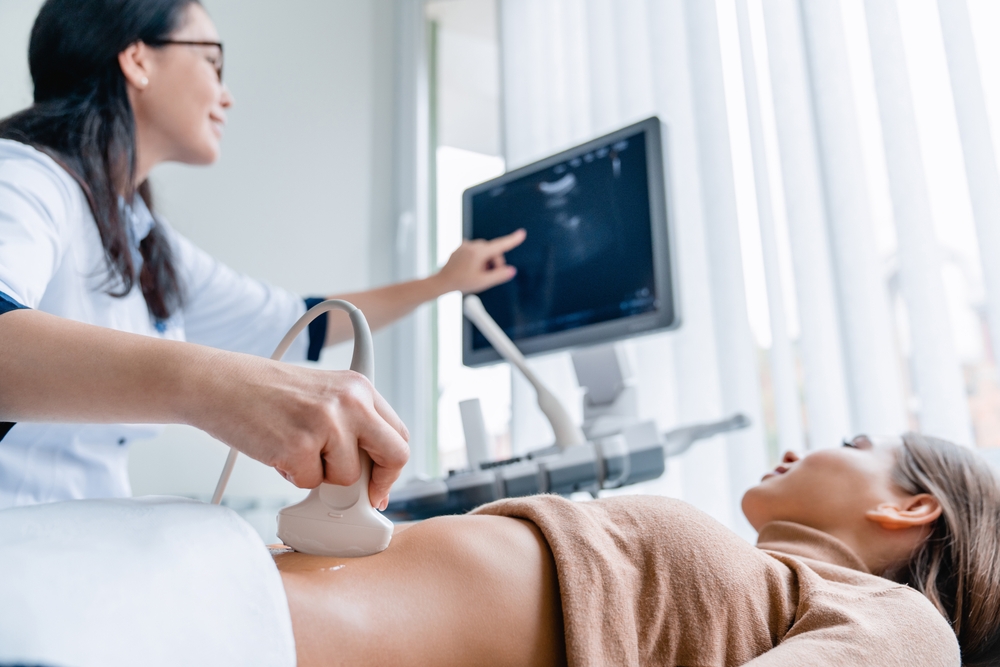
Understanding Menopause
Menopause marks the time in a woman’s life when her menstrual cycles permanently cease, typically occurring in the late 40s or early 50s. This natural biological process signifies the end of fertility and is diagnosed after 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. At Physicians for Women, we provide comprehensive care to help manage this transition. Menopause involves various physical and emotional changes due to fluctuating hormone levels. These changes can include hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness, which vary greatly among women.
Managing Menopause Symptoms
Managing menopause symptoms involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical treatments. At Physicians for Women, our healthcare providers may recommend lifestyle changes such as a nutritious diet, regular exercise, and improved sleep habits to alleviate symptoms. Medications, including hormone replacement therapy (HRT), can also be effective in reducing symptoms like hot flashes and vaginal dryness. Additionally, innovative treatments like the FemiLift™ laser procedure can address specific issues such as vaginal discomfort and dryness, promoting cell regeneration and improved blood flow.
Benefits of Comprehensive Menopause Care
The benefits of comprehensive menopause care at Physicians for Women include personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs. Our approach aims to improve your quality of life by managing symptoms effectively and providing support throughout this transition. By addressing both physical and emotional aspects of menopause, we help you navigate this phase with confidence and ease. Our team is dedicated to offering the latest and most effective treatment options to ensure your well-being.
Key Features of Menopause Care
- Comprehensive medical evaluations.
- Personalized treatment plans.
- Lifestyle modification recommendations.
- Hormone replacement therapy options.
- Innovative treatments like FemiLift™.
Preventive Aspects of Menopause Management
- Early identification and management of symptoms.
- Regular monitoring and adjustments of treatment plans.
- Education on lifestyle changes to mitigate symptoms.
- Continuous support and counseling.
- Access to the latest treatments and technologies.
Comprehensive Support During Menopause
At Physicians for Women, we understand the challenges that come with menopause and are here to provide you with comprehensive support. Our team of experienced healthcare providers offers personalized care plans that address your unique needs and symptoms. By focusing on both preventive measures and effective treatments, we aim to make your transition into menopause as smooth and comfortable as possible. Trust us to guide you through this significant phase of life with professional and compassionate care.

Definition and Importance of Annual Wellness Visits
An Annual Wellness Visit is a preventive healthcare appointment designed to assess and maintain your overall health. These visits identify potential health issues early, manage chronic conditions, and ensure you are up to date with screenings and vaccinations. At Physicians for Women, our team provides comprehensive wellness visits to help you stay healthy and informed.
The Process of an Annual Wellness Visit
During an Annual Wellness Visit at Physicians for Women, your healthcare provider will review your medical history, conduct a physical examination, and discuss any health concerns. The visit includes measuring vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and weight. Your physician will also recommend and administer necessary screenings or vaccinations based on your age, health status, and risk factors.
Benefits and Considerations of Annual Wellness Visits
Annual Wellness Visits offer early detection of health issues, better management of existing conditions, and personalized health advice. These visits allow you to discuss any changes in your health, lifestyle, or medications. By regularly attending these appointments, you can stay proactive about your health, potentially preventing more severe problems in the future.
Common Health Concerns Addressed During Annual Wellness Visits
- High blood pressure.
- Diabetes management.
- Weight management and obesity.
- Cholesterol levels.
- Screening for cancers (breast, cervical, colorectal).
Essential Components of an Annual Wellness Visit
- Comprehensive review of medical history.
- Physical examination and vital signs check.
- Personalized health plan and recommendations.
- Screening tests and vaccinations.
- Open discussion of health concerns and lifestyle changes.
Enhancing Your Well-being Through Annual Wellness Visits
Annual Wellness Visits help in the early detection and management of health issues, ensuring you maintain optimal health. Knowing you are actively monitoring and protecting your health can provide peace of mind. At Physicians for Women, our goal is to create a supportive environment where you feel empowered to take charge of your health.
Preparing for Your Annual Wellness Visit
- Gather and bring previous medical records or test results.
- List any medications you are currently taking, including dosages.
- Note any significant changes in your health or symptoms.
- Prepare a list of questions or concerns to discuss with your physician.
- Ensure you have current information on your family medical history.

FAQs About Physicians for Women
Curious about what makes our practice unique? Here are some questions our patients often ask:
What will care look like with an OB/GYN?
Our board-certified OB/GYNs have the experience and knowledge to handle any situation that may arise during pregnancy. Whether it’s a normal pregnancy or a complex one, our OB/GYNs will be there to guide you through every trimester for a safe delivery. They are committed to providing the highest standard of comprehensive, evidence-based, collaborative care. Throughout your pregnancy, they will take the time to get to know you, and you will also get to know each of the providers as you progress through your trimesters. The mission of our OBGYNs is to ensure that you don’t feel like just a number and that you feel supported and safe throughout your pregnancy.
What insurances do you accept?
We accept Aetna, Blue Cross Blue Shield, Cigna, Humana, Quartz, The Alliance, Tricare, WPS, Beech Street, and more. To read more about our accepted insurances, please visit our Patient Center tab and click “Insurances Accepted”.
I am pregnant. What are the first steps?
First things first, congratulations! We are so happy to have you consider our clinic for the care of you and your growing family. The first step is to schedule your dating appointment with us. Once you have scheduled, please go to our Patient Center tab and click “Patient Forms”, to get to our Welcome Packets. It will include information such as early pregnancy FAQs, ultrasound information with timing and values, fetal movement records, and more! To schedule your dating visit, please call our office at (608) 227-7007 or request an appointment on our website. We can’t wait to see you!
What are your hours?
Our hours are Monday through Thursday 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. and Fridays 8:00 a.m. to 12:30 p.m.
How can I make an appointment?
You can make an appointment with us online by using our request appointments button on the homepage, by using our Contact Us tab, or by calling our office at 608-227-7007. We are happy to assist you!
What paperwork do I need to fill out before my appointment?
If you’re a new patient, you’ll need to fill out our new patient paperwork before your appointment. This usually takes about 30 minutes, so we kindly ask new patients who prefer to fill out their paperwork at our clinic to arrive up to 30 minutes early. If you’d like to fill out your paperwork in advance, please head to our Patient Center tab at the top of the screen and click on “Patient Forms.” You’ll find three forms to fill out: the Confidential Health History, Registration Form, and our Voicemail Consent. If you complete your paperwork before coming to our clinic, we ask that you arrive 15 minutes early.
What types of payment methods do you accept?
Physicians for Women accepts MasterCard, Visa, American Express, Discover, Debit Card, Cash, and Check. If you have any questions about your preferred payment method, please give us a call at 608-227-7007.
What sets Physicians for Women apart from other OB/GYN practices?
Our blend of comprehensive services, personalized care, and advanced technology creates a unique healthcare experience. We’re not just treating patients; we’re nurturing relationships and empowering women through every life stage.
Can you accommodate specific preferences for my birthing plan?
Absolutely! We believe in empowering you to shape your birthing experience. From natural births to gentle C-sections, we work closely with you to create a birthing plan that aligns with your wishes while ensuring the safety of you and your baby.
How do you support women going through menopause?
Our menopause care is tailored to each woman’s unique experience. We offer a range of treatments, from hormone replacement therapy to lifestyle interventions, all designed to ease this transition and enhance your quality of life during this new chapter.
What should I do if I have concerns outside of office hours?
Your health doesn’t clock out, and neither do we. We offer after-hours support for urgent concerns. Our team will guide you on how to reach us when you need us most, ensuring you have peace of mind around the clock.

Your Journey to Wellness Begins Here
Embark on a transformative health experience with Physicians for Women. Your well-being isn’t just a destination; it’s an ongoing journey, and we’re honored to walk beside you every step of the way.
Don’t let another day pass without taking charge of your health. Reach out to us today, and let’s start writing the next chapter of your wellness story together. Your body, your health, your future—they deserve the best care possible, and that’s exactly what we’re here to provide.